Table of content
One of the common fundamental rules of investing and trading is the principle of diversification. There is even a common expression about this: ‘Do not put all of your eggs in the same basket’. The reasoning behind this is that if one trader or investment goes wrong, market participants will not face very high losses if they have a well-diversified portfolio. On the other hand, if traders put all of their money in one single trader, then they can easily end up losing most of their trading capital.
The Forex market is no exception to this. Instead of relying on one trading position, it is always a better idea to build a solid portfolio of currency pairs. Obviously, professional traders do not choose Forex pairs to trade at random. They are usually looking for undervalued currencies, which have the potential for future growth.
This can not be achieved without conducting proper research. It generally involves several steps. Firstly, it is essential to compare the relative nominal and real interest rates across currencies. This type of analysis is not strictly confined to the current central bank policies. The research of the latest economic indicators such as Consumer Price Index (CPI), Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth rate, the unemployment rate can be very helpful. The reason for this is that the economic performance of a nation has a significant impact on the future path of monetary policy.
Secondly, traders can determine how much the current exchange rates have diverged from the fair valuation. There are some complex formulas and indicators to measure this. However, the easiest way to do this is to check the latest Purchasing Power Parity indicators at the website of the Organization of Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) or at British financial magazine ‘Economist’ and compare it to current exchange rates.
Finally, after identifying potential currency pairs to trade, it might be helpful for traders to be aware of Forex pairs correlation. This means that some securities tend to move in the same direction. Therefore, constructing a portfolio with highly positive correlated currency pairs is not really the best way to achieve currency diversification.
Building Growth Portfolio with Forex Pairs
One of the decisive factors when it comes to the exchange rates is the central bank interest rates. Rising currency rates helps the given currency in two ways. Firstly, higher rates do mean that traders can earn higher swap rates for buying the currency, so this makes it more attractive for market participants. On the flip side of the coin, this also discourages the short-selling of the currency, since those traders who take those positions have paid higher rollover charges than before. Therefore, as a result, fewer market participants might decide to sell the currency.
The second effect extends not only to traders but investors and savers as well. As a result of higher interest rates, people can get larger percentages of returns on Certificates of Deposit (CDs), savings accounts, government bonds, and other fixed-income instruments.
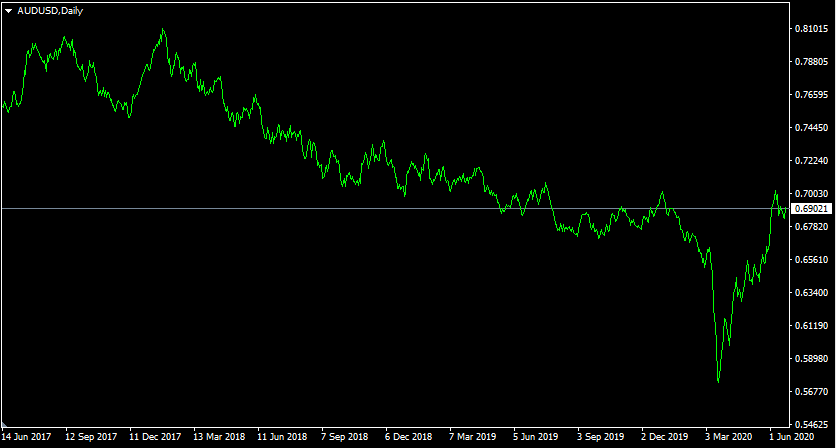
In order to illustrate this better, let us take an example from Forex major pairs. Here, on this daily AUD/USD chart, we can check the exchange rate developments this pair for the last 3 years:
Before analyzing this diagram, it can be helpful to remember where the interest rates stood in the USA and Australia back in 2017. From December 2008 until December 2015, the US Federal Reserve kept its Federal Funds rate within 0% to 0.25% range. Therefore, 0.25% was the upper on official American Interest rates. After the US economy recovered from damages of the great recession, the local central bank started considering the possibility of rate hikes. The first such decision eventually came in December 2015, followed by another rate increase a year later.
Therefore, at the beginning of 2017, the upper limit of the Federal Funds rate moved to 0.75%. This was followed by 3 rate hikes in 2017 and 4 rate increases in 2018, each by 25 basis points (0.25%).
On the other hand, the Reserve Bank of Australia has already dropped rates from 4.25% in the aftermath of the 2008 crisis, to 1.50% before the end of 2016. The central banks made no moves through 2017 and 2018.
The currency pairs in Forex are usually heavily influenced by the divergent monetary policies. AUD/USD was no exception, by June 2017 the pair traded at $0.76. At that stage, the interest rate differentials still favor the AUD, therefore, during the subsequent months, the Australian dollar made significant gains, eventually reaching $0.81 by January 2018.
However, by that time, the Federal Reserve’s consistent rate hikes had started to make a difference and AUD/USD entered a long term downtrend, which lasted for more than 2 years. After the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, both US and Australia economies suffered serious damage due to the loss of human lives, lockdowns, and travel restrictions. In order to respond to those challenges, both the US Federal Reserve and Reserve Bank of Australia dropped their respective key interest rates to 0.25%. Despite this development, the US dollar kept appreciating, with AUD/USD eventually falling all the way down to $0.57 level during March 2020.
However, at that stage, the panic selling has ended. The Australian inflation rates still remain above 2%, even at some point approaching 3%, so at some point, it is possible that the Reserve Bank of Australia might consider a rate hike. Also, several Purchasing Parity Indicators suggested that the AUD was already more than 20% undervalued against USD, by January 2020. Therefore, the market sentiment changed and the Australian dollar started to regain some of the lost ground, with AUD/USD reaching $0.69 level by June 2020.
So as we can see from this scenario, even when it comes to the most liquid Forex pairs, they are heavily influenced by central banks’ decisions. So in this case, back in 2017, a trader could have added AUD/USD to his or her Forex pairs list, since he or she concluded that the USD had a lot of potential for making substantial gains.
Need for Diversification
Here it is important to mention that the growth portfolio definition does not include having just one trade. The very meaning of the portfolio implies that a trader or an investor should have several assets at his or her disposal. So it would be much better for the market participants to have at least 3-5 positions open at the same time.
Obviously, after gathering some experience, traders can increase the size of their growth portfolio pairs in Forex to 10 or even 20 securities. However, managing such a large amount of traders simultaneously is rather difficult and requires some knowledge and experience. Therefore, having 3-5 positions at the beginning is pretty easy to manage and also can provide some diversification.

However, in order to achieve the desired result, it is important to avoid opening positions with highly correlated currency pairs. Returning to our earlier example, if a trader decides to open a short AUD/USD position, adding to this a short NZD/USD trade will not diversify a portfolio. Positively correlated Forex currency pairs meaning that they usually tend to move in the same direction. So since AUD/USD and NZD/USD are highly positively correlated, opening those two positions simultaneously will only magnify the risk exposure, rather than diversifying portfolio.
Obviously, correlated Forex pairs meaning does not imply that they always have to move in the same direction. Sometimes their paths can diverge, due to changing interest rates, geopolitical or economic events, and other factors. However, this does mean that most of the time they make similar gains and suffer similar losses.
Therefore, one growth portfolio example would be to open a short AUD/USD, long EUR/CAD, and long GBP/CHF positions. Those three currency pairs are not highly correlated with each other, so they can provide traders with a significant amount of diversity in their portfolios. Some traders might also want to add gold and silver positions to their portfolio, for the purpose of further diversification. However, it might be helpful to keep in mind that some currencies are highly correlated with those, especially when it comes to the Australian dollar and the Swiss Franc.
Finally, it is also essential to point out that there is also such a phenomenon as a negative correlation. This applies to those currency pairs which tend to move the opposite directions from each other. For example, EUR/USD and USD/CAD are highly negatively correlated with each other. Therefore, opening a long EUR/USD and short USD/CAD positions essentially represent the same side of the trade. Therefore this might not be the best case for portfolio diversification. So this is something to keep in mind when making trading decisions.
Real Interest Rate Differentials in Currency Pairs Explained
We have already discussed the major role the Central bank monetary policy can play with the Forex main pairs. However, this is not the full story. There are some high-yielding currencies, especially in the emerging markets, which still suffer from frequent depreciation. So how can we explain this?
This is exactly where the real interest rates come into play. The headline rate, published by a given central bank, is just a nominal interest rate, which does not take into account the inflation rate. Therefore, the real interest rate is calculated by the nominal rate minus the Consumer Price Index.
For example, by June 2020, the Reserve Bank of Australia holds its cash rate at 0.25%. At the same time, the latest release of the Australian Consumer Price Index showed 2.2%. This means that the real interest rate of AUD is -1.95%.
So in many cases, the differentials between real interest rates can have an even more notable impact on exchange rates, than nominal rates. To illustrate this, let us take a look at this daily EUR/SEK chart:
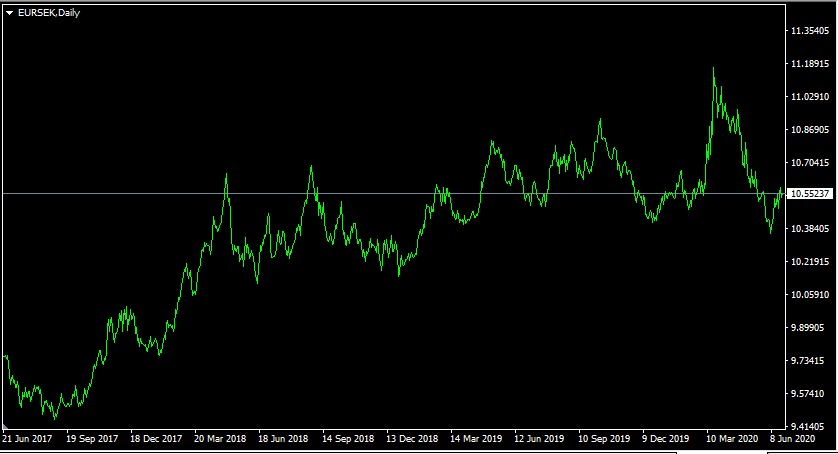
Throughout this 3 year period, the European Central Bank kept its key interest rate at 0%. On the other hand, the Swedish Riksbank has authorized two rate hikes, bridging its repo rate from -0.5% to 0%.
Logically, this should have benefited the Swedish Krona. So was that the case? Well, by June 2017, the EUR/SEK pair was trading close to 9.75 level. During the subsequent years, the Euro has appreciated steadily, eventually stabilizing around 10.52 mark. As we can see from this image, there were a lot of fluctuations, but the overall trend is in favor of a single currency. In total, during this period the Euro has gained 7.9% against Swedish Krona.
So how can we explain those surprising moves? Well, one logical explanation for this might lie in the fact that there were significant differentials in terms of real interest rates. Yes, in terms of nominal rates, they are both at zero, so there is not much of a difference in that regard. So let us move to inflation rates.
By the end of 2019, the annual inflation rate in Sweden was at 1.8%, at the same time, the Eurozone CPI, stood at 1.3%. This means that the real interest rate for SEK was -1.8% and for EUR this indicator was at -1.3%. So despite two recent rate hikes, the Swedish Krona was still at a disadvantage against the single currency, since its real interest rates were 0.5% lower than with the Euro. So this made it more appealing to traders and investors, leading to a rise in the EUR/SEK exchange rates.
Finally, before concluding this section, it is helpful to mention that unlike with negative nominal rates, central banks can enforce negative real interest rates. If someday, it was announced that deposits will pay -3%, then it is highly likely that many savers and investors will withdraw their money and move elsewhere, where they will not face those charges. On the other hand, we can see that nowadays, in Eurozone countries, the same depositors still hold money at 0% accounts and consequently lose some purchasing power of those sums, due to inflation.
So this suggests that when choosing currency pairs for a growth portfolio, it is essential to take relative interest rates into account as well, as opposed to only considering the headline nominal rates.
Finding Undervalued Currencies
Another major factor that influences even the top Forex pairs is the Purchasing Power Parity (PPP). This term is defined as the exchange rate, which equalizes the average price of goods and services between two given countries. It does not have much influence on the exchange rates in the short term, however, when it comes to the long term trading, it can have a decisive effect on the Forex market.
To illustrate this, let us take a look at this daily USD/NOK chart:
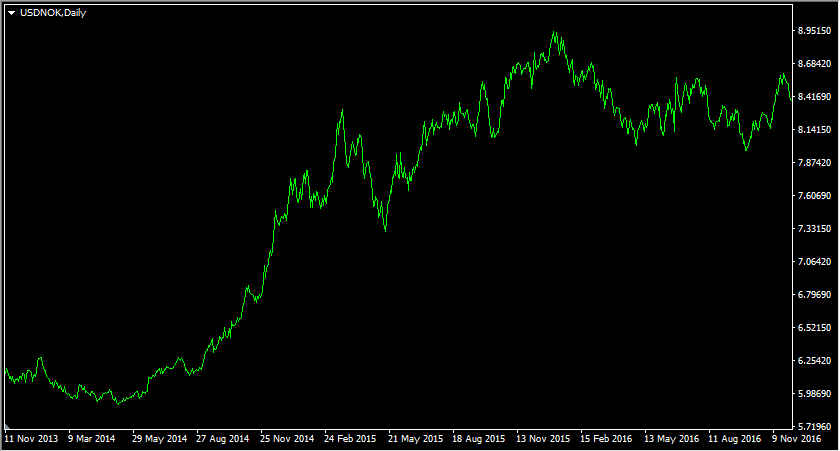
The exchange rate developments of Norwegian Krone has been a curious case. For many years, it was one of the most overvalued currencies in the world. According to the Economist, from 2002 until 2014, the currency was more than 60% overvalued against the US dollar. As we can see from the chart above, as late as May 2014, the USD/NOK was trading near 5.85. At the same time, the Economist’s Purchasing Power Parity indicators suggested that the fair value for this pair was close to 10.00 level.
The catalyst for this correction was the persistent decline in oil prices during 2014. Norway is one of the largest oil producers and exporters in the world, therefore, falling energy prices had a negative impact on the local economy, as well as on the revenues of the Norwegian government.
As a result of those developments, the USD/NOK rose steadily, reaching 7.40 level before the end of the year. This upward trend resumed in 2015, as a result, by December 2016, 1 USD was worth more than 8.40 Norwegian Krone. Nowadays, in June 2020, the USD/NOK exchange rate is even higher, currently standing close to 9.50 level. So the correction of PPP imbalances in Forex can happen with most traded pairs, as well as with more exotic currencies as well.
So if a trader opened a long USD/NOK position during this period, after recognizing the relative undervaluation of the US dollar, he or she would have gained 43.5%. In the case of 1:5 leverage that could amount to 217.5%, a very solid return for any trade.
Managing Currency Portfolio
One thing to remember here is that, even after conducting the most thorough research, traders can still get some trades wrong. It can so happen that the market might move in towards the opposite direction, or alternatively, the exchange rate might stagnate and it might take a while before the expected growth potential of a given currency could materialize.
This is why there is a need for active portfolio management. For example, if an undervalued currency rises to its PPP level, or if the central bank which manages this currency reverses its policies, then it might be the right time to close the position and lock in profits. Also if it turns out that the choice of currency pair was wrong and the trader starts losing a significant amount of investment, then it might be a good idea to cut those losses and liquidate this position.
Also, once traders construct a diversified portfolio of 3-5 currency pairs, it does not mean that they should stop exploring new opportunities. The Forex market is open for 24 hours for 5 days a week. This gives more than enough time to traders and investors to analyze the market and take advantage of the latest undervalued opportunities.

So essentially, when it comes to portfolio management, it is worth mentioning that there are no such things as best Forex pairs to trade. Instead, everything depends on the current market circumstances, such as nominal and real interest rates, economic announcements which can influence those central bank rates and currency valuations in terms of Purchasing Power Parity. Therefore, a currency pair that is stuck in ranged trading and does not present any significant trading opportunities, might become more relevant at some point in the future.
Finally, since many experts advise us to diversify, there is always a tendency for some traders to get into dozens of currencies and construct portfolios with 20 or more currency pairs. This might not be advisable for many market participants, especially for beginners. It is much easier to study 5 currencies, the fundamentals and characteristics of economies behind them. Even a combination of 5 currencies makes up 10 currency pairs, giving traders enough space to work with.
Building Portfolio of Forex Currency Pairs – Key Takeaways
- By investing most or all of their money in one trade, traders are risking large losses. Instead, many experienced traders and financial experts advise us to diversify. This can be achieved by at first choosing 3-5 currency pairs and actively managing growth portfolios, opening, and closing positions, in response to changing circumstances.
- There are a great number of factors, influencing the exchange rates. However, traders can identify undervalued currencies, by researching which central banks are likely to raise rates in the foreseeable future and which currencies have better real interest rates. Finally, the market participants can also look for those currencies which trade below the level, suggested by the Purchasing Power Parity indicators. The latest data on this subject is published by the OECD and the British financial journal ‘Economist’.
- When selecting the currency pairs for growth portfolios, traders should be aware that some currency pairs are highly correlated with each other. The one obvious example of this is the case of AUD/USD and NZD/USD, two pairs that mostly move in towards the same direction. By ignoring these factors, traders can magnify their risk exposure without even knowing it. Therefore, to avoid such a scenario, it might be better to choose currency pairs that are not closely tied together and do not have a high degree of correlation.