Table of content
Carry trading is a simple Forex strategy, which is still very popular and widely used among the traders in the market. The basic principle behind this type of trading involved borrowing a low-yielding currency in order to buy a high-yielding currency. So essentially a trader using this method aims to capitalize on the interest rate differentials among different currencies and earn some payouts in the process.
So how can a trader earn money, using currency carry trade? Well, when a market participant buys a currency with a high-interest rate and sells low-yielding currency, for every single day he or she keeps the position open, a broker pays an interest rate differential to the client on a daily basis. This is also known as rollover or interest swap, because here essentially a trader swaps the interest payments of one currency for that of the other currency.
In order to succeed with the FX carry trade strategy, it might be helpful for traders to take several steps. Firstly, before even beginning to implement those methods, it is essential to find the right broker. All those companies have different rollover rates, with some of them being much more competitive than others. By finding a broker with good swap rates, traders can increase their potential income from FX carry strategy considerably.
The second obvious step is to do research on high-yielding currencies so that a trader can earn a large amount of daily interest in those positions. This can be easily achieved by checking the latest interest rates of the world’s major central banks. Also, it is essential to ensure that the chosen currencies are not under the immediate threat of devaluation.
The next phase involves identifying the best funding currency. This does mean finding the currencies with the lowest interest rates. The reason for this is to borrow funds as cheaply as possible.
Finally, trades then can move on to opening positions and executing trades accordingly. In general, by its own definition carry trading is a long term strategy. Consequently, traders might keep their positions open for months. However, there are some scenarios, it might be better to close the trade and move on to other opportunities.
Choosing Broker with Competitive Rates
As mentioned before, the essence of the carry trading method is to capitalize on the differentials on the interest rates. For the sake of clarity, let us take a practical currency carry trade example. By June 2020, the European Central Bank holds its key interest rates at 0%. At the same time, the Bank of Russia’s interest rate stands at 5.5%. So as we can see from this example, the interest rate differential here would be 5.5%. However, this does not necessarily mean that the rollover, which the broker will pay to the client will be exactly the same.
One thing to remember here is that the brokerage companies do take their commissions from those types of trades as well. So the actual swap rate, paid to customers is usually lower than the interest rate difference between the two given currencies. Many brokerage companies even have a carry trading calculator on the websites, so that traders can estimate their potential earnings, even before opening any positions.
So returning to our example, let us suppose that after conducting a thorough analysis, some traders have decided to open a short EUR/RUB position, which trades at 78.00, for the purpose of Forex carry trading with 1 standard lot, which represents 100,000 units of currency. So this transaction will involve the sale of 100,000 EUR and the purchase of 7,800,000 RUB.
Let us further suppose that according to the broker’s carry trading calculator, traders will receive 14.80 EUR for each day of having such a position open. So what is the annual interest rate here? Well, if we multiply the above-mentioned amount to 365, the number of days in a year, the total sum will be 5,402 EUR. So the actual effective interest rate here will be approximately 5.4%. So in this particular case from the interest differential of 5.5%, the broker commission would be 0.1%, while the rest of the difference is passed on to the client.
Another important detail to consider here is the fact that brokers do not pay rollovers on Saturdays and Sundays. Instead, they give triple rollovers to their clients, in order to account for the missing payments during the weekends.
So this sounds similar to high-yielding savings accounts. However, there are two distinct differences between the carry Forex trade and bank deposit accounts. Firstly, in the former case, the principle of the invested amount is not secure and it is pretty much subject to market fluctuations. So the value of their investment will fluctuate depending upon the exchange rate movements.
On the other hand, in the Forex market, people can make use of leverage. Returning to our earlier example, if traders open a short EUR/RUB position with 1:10 leverage, their annual rate of return will be 54%, instead of 5.4%. It goes without saying that this is indeed a quite lucrative investment, but as mentioned before, it does have its own risks.
This is why it is essential to find a broker that has very competitive swap rates. Even a small percentage difference can add up to a significant sum in the long term. Fortunately, all major Forex brokers have their rollover rates available on their website, so traders can compare different companies and choose the one, which pays the highest returns for interest rate differentials.
Choosing High-Yielding Currencies
According to the carry trading definition, the process involves buying high-yielding currency. In fact, it is such a crucial element that without this it is impossible to use this Forex strategy.
This essentially requires a research process, which is very straightforward. Nowadays, many Forex news websites list the key interest rates of the world’s central banks and update those pages on a regular basis. Here traders can take note of several currencies, selecting them as ‘candidates’ for carry trading strategy.
The next stage would be to research those selected currencies for more details. For example, finding out whether the current inflation rate is within the range of the central bank’s intended target, or whether there are major changes in the economy of the currency in question. Professional traders do this with a carry currency strategy to make sure that they choose those currencies, the central bank of which is not likely to reduce rate significantly over the foreseeable future.

Also, it is vital to make sure that the given currency is not currently engaged in some sort of downtrend against the major currencies. There are some high-yielding currencies, which are constantly depreciating against their peers, so this is something to keep in mind.
If traders ignore those steps, they can easily end up in a situation where they see their returns diminished over the months, because of the repeated rate cuts, eventually rendering the entire trade unprofitable. So this type of due diligence is a precautionary step to guard against those unpleasant surprises.
On the other hand, it will be very helpful if traders manage to find high-yielding currencies, which are likely to experience rate hikes in the future. This can happen for example, when the Consumer Price Index is significantly above the central bank’s target. So it can be always handy to check the latest inflation dynamics of those high-yielding currencies, before choosing the ones for implementing Forex carry trade strategy.
For example, by June 2020, the high-yielding currencies are the Turkish lira with an interest rate of 8.25%, the Russian Ruble (5.50%), the Mexican Peso (5.50%) and the South African Rand (4.75%).
For many years, due to high-interest rates, the Australian dollar and New Zealand dollar have been traders’ favorite currencies for currency carry strategy. However, by early 2020, the central banks of both of those currencies reduced their rates at 0.25%. So trades can still earn some returns on those, but it will be much smaller, compared to the previous year. However, if at some point in the future the Reserve Bank of Australia and Reserve Bank of New Zealand decide to hike rates, then AUD and NZD can once more become attractive for currency carry trade strategy.
So as we can see there are not that many opportunities at the market for carry traders. Therefore, some of them might have turned to exotic currencies to fill the gap. Among this category, the Turkish lira seems the most attractive option, since it has the highest yield. However, to check for latest trends let us take a look at this daily EUR/TRY chart:
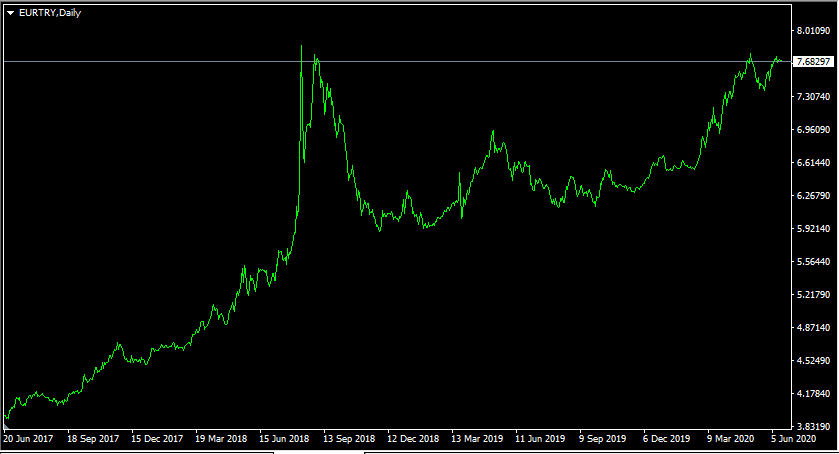
As we can see from the above diagram, the long term trend here is very clear. 3 years ago, back in summer 2017, the Euro traded near 3.90 mark, during the subsequent months, the single currency made massive gains against the TRY, with a brief correction, back in 2018 and by June 2020 it has reached 7.68. This means during this 3-year period the EUR/TRY pair has risen around 97%. This suggests that on average, the Turkish lira was depreciating by more than 25% per year against the single currency.
Also, we can not identify any potential reversal points, as the EUR/TRY pair maintains its uptrend. Therefore, we can conclude that at the moment the Turkish lira might not be the best choice for carry trading since it is likely that those trends might continue and traders might suffer serious losses as a result.
Let us now return to our EUR/RUB example, the rate differential seems quite attractive, so let us take a look at the daily chart of this pair:
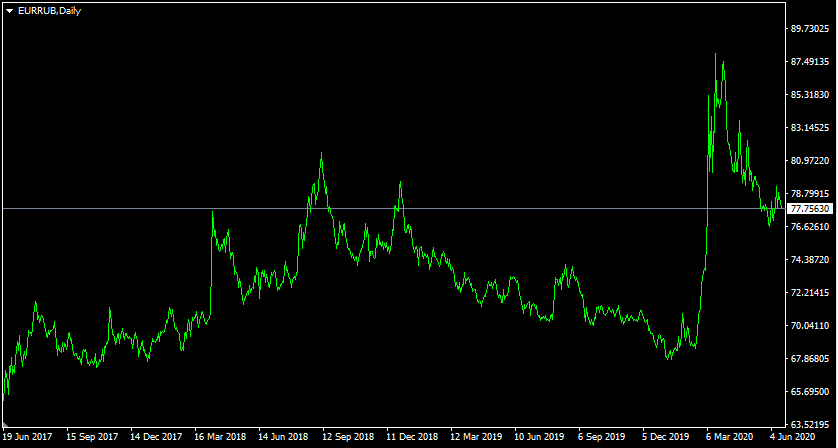
As we can see here also the long term trend tends to favor the single currency. However, the advantage here is not so clear cut as in the previous case.
3 Years ago, EUR/RUB was trading just above 66 level. The pair has risen steadily until reaching 81 mark in September 2018. However at this point, EUR/RUB experienced a major correction and by December 2019, dropped all the way down to 68 level. The pair skyrocketed to 88 level during February-March 2020, however, here again, this was followed by a sharp correction, eventually returning the pair close to 78 mark.
Therefore, during the last 3 years, the single currency has risen by 18%. This suggests that the average appreciation of the EUR/RUB was just above 5%. So as we can see, shorting EUR/RUB might not be among optimal currency carry trade strategies, however, it is certainly a better option than doing the same with EUR/TRY.
Choosing Funding Currency
The second essential element for successful carry trade is choosing so-called the ‘funding currency’. This is the currency in which traders borrow money to buy higher-yielding currencies. Consequently, the rules here are completely opposite to what we have discussed in the previous section. So essentially a trader is looking for currencies with lowest interest rates and for the ones who are not currently engaged in an uptrend.
For at least two decades the Japanese yen has been traders’ favorite funding currencies, because of its very low internet rates. At the moment the Bank of Japan keeps rates at -0.1%, so it is still a very useful currency in that regard. The Swiss Franc is another obvious choice since the Swiss National Bank has reduced rates to -0.75%.
Here it is helpful to point out that the fact that the above-mentioned central banks introduced negative interest rates does not necessarily mean that brokers can borrow CHF at -0.75% or JPY at -0.1%. In most cases, the effective rate is still zero. This means that for example, the effective interest rate differential between the Australian dollar and Swiss Franc would be 0.25%, rather than 1.00%.
The reasoning behind this is very simple. Swiss National Bank can officially declare a negative interest rate policy, but it can not simply enforce it on households and corporations. Instead of savers paying banks interest for the privilege of holding deposits with them, many clients will either withdraw their money or transfer it to those current accounts where they will not be charged those rates.
It is not also realistic to expect from banks to start paying interest rates on loan balances of individuals and corporations, suffering heavy losses in the process. So for practical purposes, when calculating possible swap rates, it can be handy to count the yields of currencies with negative interest rates as 0%.
After the European Central Bank reduced rates to zero back in 2016, the Euro also became a popular funding currency for carry trades. So all those three currencies, EUR, JPY, and CHF now offer very low-interest rates, but the question is: which currency is currently the best option? To answer this question, let us take a look at this daily EUR/CHF chart:
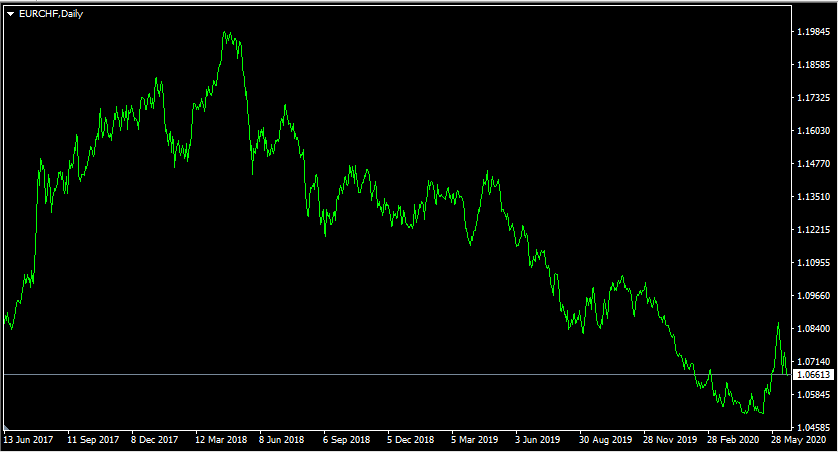
As we can see from the image above, the Swiss franc is clearly in a long term uptrend against the Euro. Back in June 2017, the pair was trading close to 1.0850. At first, the Euro started to rise consistently, eventually peaking at 1.20 level by Apri, 2018. However, this tendency turned out to be quite short-lived. From May 2018, the pair settled for a long term downturn, eventually dropping all the way down to 1.05 level by May 2020.
After this development, the Euro did try to break out of this downward channel, however, the attempt eventually failed and the single currency is back to its downtrend, currently trading just below 1.07 mark.
Since 2017 the single currency is also losing ground against the Japanese yen, however during the last 12 months the exchange rate stabilized and consequently, the EUR/JPY was mostly confined within 116 to 122 range.
Therefore, we can conclude that at the moment Euro is indeed one of the best funding currencies, available at the market. At the same time, the Japanese yen can also be a decent choice, since after 2012 the Bank of Japan is aggressively pursuing its 2% inflation target and is likely to take decisive measures to counter the threat of deflation. The central bank did manage to keep CPI close to 2% for several years, but recently it fell close to 0%. Therefore it is likely that policymakers at the Bank of Japan will keep rates low for years to come.
However, it is useful to point out that the circumstances can always change and at some point in the future, there is a distinct possibility that other currency takes this place. In fact, there are at least 10 major economic indicators, which can have a significant effect on the exchange rates.
How to Manage Carry Trade Positions?
After identifying the best currencies to carry trades, there are still several things to consider. Firstly, one of the common mistakes traders make at this stage is to use very high leverage, which can be very risky and lead to severe losses. In general, carry trading is a long term strategy and during those months, the given currency pair can experience a significant degree of fluctuation.

For example, if a trader uses 1:400 leverage, it only takes a 0.25% change in the currency pair against the opened position, for it to be wiped out. In the US, after the regulatory reform, the maximum amount of leverage for major currencies was reduced to 1:50. However, still at this rate, if a market moves against the trader by 2%, the position can be closed down.
In order to reduce those obvious risks, traders can confine their leverage levels within 1:1 to 1:10 levels. The exact method of handling such trades depends on the amount of capital under the disposal of an individual. For example, traders who have large sums available for trading can go for 1:1 leverage. In this case, it is nearly impossible for trader’s positions to be wiped out since currencies usually do not go to zero. So this can give peace of mind to some market participants.
On the other hand, if a trader has a smaller amount of capital and chooses 1:10 leverage, it does require more active management. If the currency, chosen to carry trade depreciation significantly, then a trader might consider cutting his or her losses, before things get out of hand.
Also if the given currency appreciates and crosses deep into the overvalued territory, then traders might decide to close the position, locking in those gains and explore some other profitable opportunities elsewhere.
Essentials of Carry Trading – Key Takeaways
- According to the carry trade definition, this Forex strategy involves borrowing the low-yielding currency in order to buy the high-yielding currency and capitalize on those interest rate differentials. As a result, a broker keeps some portion of this difference as a commission and deposits the rest on client’s accounts on a daily basis. This is also known as rollover or interest swap. Since the Forex market is closed during weekends, triple rollovers are given on Wednesdays, to account for those two weekdays.
- A successful carry trade strategy involves choosing a high-yielding currency, which is not engaged in a downtrend against other currencies and its central bank is not likely to reduce rates significantly over the foreseeable future. The second component of this is to find a funding currency. This should be a very low-yielding currency, which is not engaged in an uptrend and also the central bank of which is not likely to hike rates considerably.
- Carry trade is essentially a long term strategy. Therefore, the exchange rate of the given currency pair can change considerably. Consequently, it might be a good idea for traders to confine their use of leverage to the 1:1 to 1:10 range, for the purpose of reducing risks and better financial flexibility.