Table of content
When it comes to Forex trading, some market participants might have a hard time deciding whether they should limit their trading to only major currencies, or alternatively open some positions with exotic currencies as well.
There are indeed some valid points from both sides of the argument. Therefore, for traders to make an informed decision, we will take a look at the special characteristics of exotic currencies.
One of the most important advantages of trading exotic currencies is the fact that in many emerging market countries, the interest rates are much higher than in developing nations. This gives traders some opportunities to earn a daily income from carry trades on a regular basis.
In addition to that, it is worth noting that in terms of purchasing power parity and other indicators many emerging market currencies are considerably undervalued against major currencies, hence the potential of their appreciation.
Everything else being equal, the exotic currency pairs generally tend to be more volatile than major pairs. This provides traders with an opportunity to earn higher returns from winning trades.
Despite all of those advantages, trading exotic currencies do have some downsides as well. Firstly, it is important to keep in mind that the average inflation rates in emerging markets are considerably higher than in developed countries. This does have long term implications, leading to depreciation of some of the exotic currencies against the major currencies.
Another major issue with trading exotic currencies is that they are generally much less liquid compared to major currencies. Consequently, in many cases, the spreads brokers can offer on those pairs are much wider than with Forex majors.
Finally, it is worth mentioning that generally speaking the market movements with exotic currencies tend to be less predictable than major currencies. There are several reasons for this, one of them being the fact that there is an internal demand in those countries for more stable currencies as a store of value. Consequently, many ordinary citizens selling and buying foreign currencies can have a sizable impact on exchange rates.
Let us now go through each of those advantages and disadvantages in more detail.
Higher Interest Rates
One of the main reasons why some traders might be interested in opening trades with exotic currencies is that the interest rates in many developing countries can be considerably higher than in developed nations.
This can be very attractive for many market participants, especially carry traders. The fact of the matter is that a number of central banks have already adopted a near-zero interest rate policy in response to the 2008 Financial Crisis. During the subsequent years, some of them, including the US Federal Reserve, have started normalizing the policy, raising rates gradually.
Yet this process was cut short by 2020 when in response to the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic all major central banks have returned their rates close to zero. In fact, some of them, including the Bank of Japan and the National Bank of Switzerland went as far as to openly adopt negative interest rates for years.
The result of this development is the fact that by April 2020, all major currencies in Forex: the US dollar (USD). the Euro (EUR), the British Pound (GBP), the Japanese yen (JPY), the Australian dollar (AUD), the Canadian dollar (CAD), the Swiss franc (CHF), and the New Zealand dollar (NZD), have their interest rates at 0.25% or lower. In fact, the Swiss franc is leading the way in terms of record-low interest rates, with SNB maintaining rates at -0.75%.
It goes without saying that such record-low interest rates across the board can be a piece of welcome news for mortgage holders. However, this has also created serious problems for savers and carry traders. For example, back in 2007, it was possible for depositors to easily find savings accounts and certificates of deposit, also known as CDs, which have yielded 5% or higher. Nowadays it is no longer possible to find those lucrative savings instruments. In fact, the best deal most savers can find is a 1% CD with some online banks.
It is also worth mentioning that before 2008, many traders earned decent returns by carry trades, by opening long AUD/JPY and NZD/JPY positions. At that time, the interest rates in Australia and New Zealand were fluctuating between 4% to 7.25%, while the Bank of Japan held rates at 0.25%. This has created a lucrative carry trade opportunity for market participants. They could borrow at a cheap rate in yen and invest it in the Australian dollar or New Zealand dollar, profiting from those large interest rate differentials.
However, those lucrative opportunities finally disappeared in March 2020, as both the Reserve Bank of Australia and Reserve Bank of New Zealand lowered their key interest rates at 0.25%. The Bank of Japan now holds rates at -0.1%. So, if we factor in broker commissions, traders can still earn 0.1% to 0.25% returns with AUD/JPY and NZD/JPY. However, those returns are tiny, compared to 4% to 7% yields, carry trades achieved before 2008.
In order to observe the impact of those factors on the Forex market, let us take a look at this weekly NZD/JPY chart:
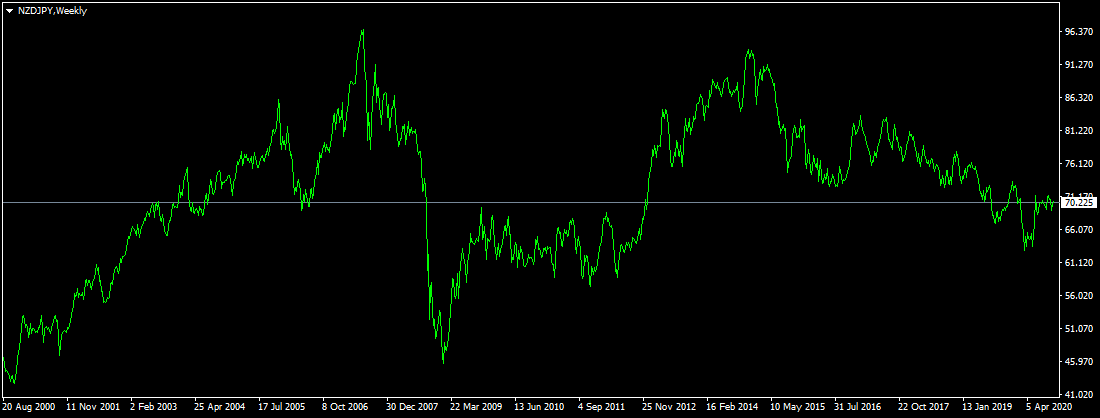
As we can see from the chart above, back in 2000, the NZD/JPY pair was trading just below 45 level. During the subsequent years, the New Zealand dollar has made steady gains, eventually rising all the way up to 96 level during the Summer of 2007. However, as the Reserve Bank of New Zealand started cutting rates in response to the economic downturn, the NZD has lost its appeal for most of carry traders.
The result of this development was the crash of the NZD/JPY exchange rate, dropping all the way down to 45 level. So this means that in a relatively short period of time, all 7 years’ worth of gains has been wiped out. Despite this collapse, the New Zealand dollar has gradually recovered its position, eventually getting above 90 level with the Japanese yen in 2015. However, as the Reserve Bank of New Zealand has continued its rate hikes, the NZD/JPY pair once more started losing its ground, eventually dropping all the way down to 70 by September 2020.
Consequently, it is not surprising that nowadays many carry traders are looking beyond major currencies to find some opportunities. There are indeed many exotic currencies, which offer higher interest rates to the market participants. For example, by September 2020, the Russian ruble (RUB) still yields 4.25%, the Mexican peso (MXN) – 4.25%, South African Rand (ZAR) – 3.50%, and Turkish lira (TRY) – 10.25%.
Therefore, by opening short USD/RUB, EUR/RUB, USD/MXN, or EUR/MXN positions, depending on the brokerage company, the market participants might be able to earn something close to 4% annually on carry trades. Consequently, this can offer an opportunity for traders to earn some decent returns by carry trading.
Here it is also worth noting that central banks in those developing countries are generally unlikely to adopt near-zero interest rate policies in a foreseeable future. This is because the average inflation rates in those countries are considerably higher than in developed countries. Consequently, if policymakers in those countries tried to impose near-zero interest rates on commercial banks, then it can likely lead to high levels of inflation and can potentially make it much more difficult to maintain the price stability in the long term.
Undervalued Opportunities
Just like with individual stocks in the stock markets, some market participants are analyzing different currencies in order to find the one which is undervalued. In order to do so, the analysts and other market participants are using the purchasing power parity indicator, also known as the PPP. The PPP essentially represents an exchange rate at which the average prices of goods and services will be equalized between the two given countries.
There is no single universally accepted measure of PPP. One of the most popular measures of this indicator is published by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, also known as the OECD. This organization publishes reports on an annual basis which lists dozens of currencies and their PPP levels in relation to the US dollar.
Another popular measure of the PPP is published by the British financial magazine the Economist. The report is published on a semi-annual basis and lists the PPP levels of dozens of currencies in relation to the US dollar, the Euro, the British pound, the Japanese yen, and the Chinese yuan.
What those reports typically show is the fact that at any point in time, there are dozens of different exotic currencies, which are considered to be undervalued against the major currencies. This means that the price levels for goods and services in those countries are considerably cheaper than in the developed countries. This means that those currencies do have a potential for a sizable appreciation against major currencies.
It goes without saying that this does not guarantee that all those exotic currencies will definitely gain ground against Forex majors. However, if traders can identify those emerging market economies with a decent growth potential, then it is possible to profit from those undervalued opportunities. This can be especially useful for long term traders, who typically hold positions open for an extended period of time.
Higher Volatility
One way in which the Forex market differs from the stock market is that the former one is much less volatile than the latter. However, those people who are looking for more volatility in the Forex market might consider trading the exotic currency pairs.
The higher volatility in the case of the emerging market currencies mainly comes from two reasons. Firstly, the exotic currency pairs have much lower amounts of liquidity than Forex majors. This means that the influence of each transaction within the given exotic currency pair is much larger compared to Forex major pairs.
In addition to that, it is helpful to keep in mind that central banks in those countries make much larger adjustments in the key interest rates, compared to policymakers managing major currencies. For example, such major central banks as the US Federal Reserve or the European Central bank typically adjust their rates by 25 basis points, especially when it comes to the rate hikes.
On the other hand, such central banks as the Bank of Russia, Bank of Mexico have very often made 50 basis point or even 100 basis point adjustments in the monetary policy. The main reason for this is the fact that in emerging markets the inflation rates tend to be very volatile and consequently this requires an adequate response from the policymakers.
In order to illustrate this higher degree of volatile with the exotic currencies, let us take a look at this daily USD/MXN chart:
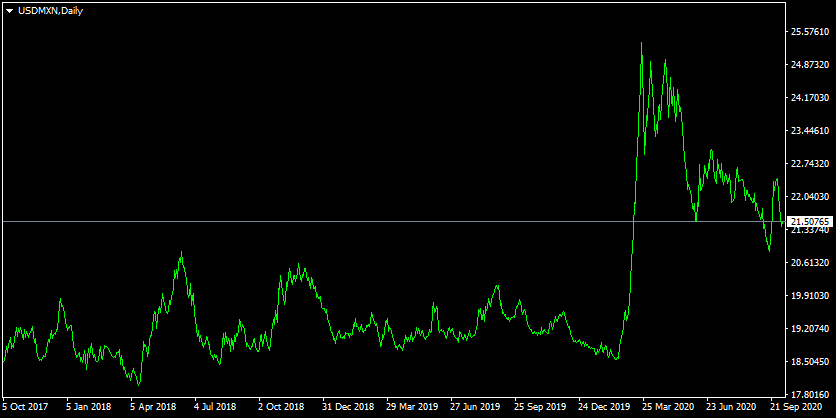
As we can see from the above diagram, back in October 2017, the pair was trading close to 18.40 level. As we can see during the subsequent months the USD/MXN pair experienced a significant amount of volatility, mostly trading within the 18 to 21.50 range. This means that during this period there was up to 19% variation in the exchange rate.
However, after the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, the pair has become even more volatile than before. The initial reaction of the market was the sharp depreciation of the Mexican peso, with USD/MXN rising all the way up to 25.40 before the end of March 2020. This means that just in a one month period, the USD has risen by 37% against the Mexican peso.
Yet, after reaching such extreme levels, this type of panic selling ceased at the market and the Mexican currency began to regain some of its lost ground. By the end of September 2020, the pair traded close to 21.50 level.
So as we can see from this example, exotic currency pairs can be very helpful trading instruments for those traders who have high risk tolerance and who aim at maximizing their returns by trading highly volatile securities.
Higher Average Inflation Rates
So far we have seen that trading exotic currencies can certainly have some notable benefits. However, it is important to understand that trading those types of currencies also has some downsides as well.
The first thing to mention about this is the fact that the average inflation rates in developing countries are considerably higher than in developed countries. For example, when it comes to the majority of major currencies, the average CPI rate during the last couple of decades would be close to a 2% to 3% range. On the other hand, in the case of exotic currencies, the average inflation rates can reach 4%, 6%, or in some cases even be above 10%. This creates some significant inflation rate differentials between major and exotic currencies.
This is exactly where the purchasing power parity once more comes into play. The fact of the matter is that when the inflation rates over the years in one country are higher than in the rest of the world, its goods and services become more expensive. As a result, the demand for those products fall and the currency tends to depreciate.
The main effect of this development is the fact that in the long term, a significant portion of exotic currencies tends to depreciate against the major currencies. Returning to our previous example of the USD/MXN currency pair, it is worth noting that back in 2000, 1 USD was worth 9.4 Mexican pesos.
After 20 years, the USD/MXN exchange rate has risen to 21.50. In other words, during those two decades, the US dollar has appreciated by approximately 129% against the Mexican peso. One of the main reasons for this is the fact that the average inflation rates in Mexico are considerably higher than in the United States.
According to the purchasing power parity theory, the currencies with lower inflation rates in the long term tend to appreciate against currencies with high inflation rates. As we can see from the previous example, the actual data generally tends to support this theory.
This creates problems for those traders who open positions with exotic currency pairs on a regular basis and holds them open for extended periods of time. For example, some traders might decide to open the short USD/MXN, USD/RUB, or USD/TRY positions and hold them open as a part of carry trade. Or alternatively, they might open those types of trades, hoping that because of their undervaluation, those currencies might appreciate against the US dollar, the Euro, or any other major currencies.
It is true that considering the current interest rate differentials, traders can earn substantial daily income by opening short positions with USD/MXN, USD/RUB, USD/TRY, and many other exotic currency pairs.
However, the main problem here is the fact that due to inflation rate differentials and some other factors, the majority of those currencies are engaged in a long term downward trend against the US dollar and other major currencies. Consequently, traders might take some significant amount of losses because of the long term depreciation of the emerging market currencies.
This tendency might have very little impact on scalpers and day traders, however, for those market participants who prefer swing or long term trading strategies, this is definitely something to be aware of when making trading decisions.
Wider Spreads
One of the disadvantages of trading exotic currencies which has to be mentioned is the fact that spreads on those types of securities generally tend to be wider than compared to the Forex majors.
Now, the fact of the matter is that Forex brokerage firms are able to offer tighter spreads for Forex majors for several reasons. Firstly, it is worth pointing out that major currencies are very liquid. They are widely available at the market in large quantities and they are exchanged in large amounts on a daily basis. Therefore, this gives brokers an opportunity to access liquidity in those currencies at a low cost.

In addition to that, it is helpful to point out that since major pairs are so liquid, brokers can earn a decent amount of income even with smaller spreads. For example, EUR/USD has been one of the most liquid currency pairs in the market for years. Consequently, brokers can still earn a decent amount of income from this pair even with 1 to 3 pips spreads, since there are thousands of traders opening positions with EUR/USD at any given time.
On the other hand, this is not necessarily the case with exotic currency pairs. The number of traders trading those pairs are considerably smaller. Consequently, the brokerage firms are applying wider spreads to those pairs in order to make it worthwhile for them.
This situation also extends to swap-free accounts. What happens with those types of accounts is that traders here are limited to trading major and minor currency pairs, without them having to pay any rollover fees for keeping positions open overnight. However, if traders wish to trade exotic currency pairs, then they have to give up their swap-free privileges and pay rollover fees just like with the regular trading accounts.
So why is this the case? Well, as mentioned before, the interest rates with the majority of the exotic currencies are considerably higher than in the case of major currencies. So if traders want to open long positions with USD/MXN, USD/ZAR, USD/TRY, or other pairs, then the brokerage company has to pay interest to the liquidity providers for holding those positions open overnight.
Consequently, what happens here is that brokerage companies pass on those interest costs to their clients, so the firm does not have to pay for those costs. However, if the brokers extend swap-free trading to exotic currency pairs as well, then they have to cover those costs from their own funds. Since the interest rate differentials between the major and exotic currencies are significant, over time this expense can easily add up to a massive amount, most likely leading to serious losses for the brokerage firm.
Therefore, in order for brokers to avoid those losses, they tend to limit swap-free accounts to major and minor currency pairs, where the interest rate differentials are much smaller compared to the case of exotic currencies.
Those factors create problems for two categories of traders. Firstly, trading exotic currencies might be problematic for scalpers. The main reason for this is the fact that as mentioned before, they tend to have wider spreads.
Now, this might not be such a serious concern for the long term traders. However, it is worth remembering that scalpers have short time frames for their trades, ranging from 1 to 15 minutes. In most cases, currencies do not make very large moves in such short periods of time. Consequently, scalpers usually have small profit goals, typically targeting 5 to 15 pips in a single trade.
Therefore, this type of strategy is unlikely to work with those currency pairs which have wide spreads, since in those cases most of the potential earnings will most likely be consumed by those types of commissions.
Trading exotic currencies might also not be a recommended option for those market participants who typically hold positions for extended periods of time. For example, let suppose that after some detailed technical and fundamental analysis, some traders decided to open the long USD/MXN position and keep the trade open for several months, in anticipation of the rise in the value of the US dollar.
The obvious problem here is that as mentioned earlier it is quite difficult to find a brokerage firm, which offers swap-free accounts and exotic currency pairs. Consequently, they have to pay rollover fees on a daily basis.
Now, according to the latest data, the interest rate differentials between those two currencies is close to 4%. So this means that if traders are using 1:1 leverage, then they have to pay the equivalent of 4% of the size of the trade in order to keep this position open for a year.
At the same time, if those market participants are using 1:20 leverage, then their effective rate of swap interest payments will be 80%. Even if traders only hold this position open for 3 months, the size of the overall swap payments will be close to 20%. It goes without saying that this can be very damaging for trading accounts of those market participants. It is highly likely that any gains they make from this trade will be more than offset by daily interest payments, they have to pay over an extended period of time.
Less Predictability
One of the interesting characteristics of exotic currency pairs is the fact that they tend to be less predictable compared to Forex majors. One of the most important reasons for this is the fact that there is a significant difference in how people save money in developing countries and in emerging markets.
What happens in countries like in the United States, in the UK, or in Eurozone nations is that people there are using stable currencies, so they generally tend to save money in local currency. This means that people in the United States mostly save and invest in US dollars, in the United Kingdom most citizens do so in British pounds and so on.
This is not necessarily the case with the developing countries. The local currencies in those countries tend to have high inflation rates and also tend to fluctuate significantly against the major currencies.
Consequently, it is not surprising that many people in emerging markets prefer to store their savings in foreign currencies. After all, losing 5% to 15% annually due to inflation with local currency is not a very appealing proposition for many investors.
Therefore, many people in those countries prefer to store their savings in US dollars, Euros, or in British pounds, where the average inflation rates are close to the 2% to 3% range. This allows them to retain most of their purchasing power and also benefit from the stability of those major currencies.
This means that there is a considerable demand for foreign currencies in those countries. As a result, there are large amounts of transactions involving the local and foreign currencies on a daily basis, which can have a significant impact on the Forex market.
For example, if due to some political or financial factors the economic conditions in a country worsens, this might lead to a surge in demand for foreign currencies, with the people buying those to shelter their savings from instability and devaluation. The results are quite predictable, as people by more foreign currency, the local currency tends to depreciate.
On the other hand, prior to vacations and holidays, people might sell some of their foreign currency holdings to spend some of their savings on those occasions. This tends to benefit the local currency and can lead to its appreciation.
Now the main problem for Forex traders is that there is no economic calendar available which can capture all of those details. Therefore, there are too many variables when it comes to the exchange rates of exotic currency pairs. This makes it very difficult to make accurate predictions. Therefore, it is not surprising that emerging market currencies very often do make quite unpredictable moves,
Trading Exotic Currencies – Key Takeaways
- Exotic currency pairs are defined as any pair which includes any currency outside 8 major currencies: the US dollar, the Euro, the British pound, the Japanese yen, the Swiss franc, the Canadian dollar, the Australian dollar, and the New Zealand dollar.
- One of the upsides of trading exotic currencies is that many of them have much higher interest rates than major currencies. This allows the market participants to use those currencies for carry trades. As a result, they can profit from interest rate differentials and earn income from swaps on a daily basis. Emerging market currencies became even more popular for carry trades after the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, as all major central banks have lowered rates to 0.25% or lower.
- Trading exotic currency pairs do have their own disadvantages as well. Firstly, it is worth noting that generally speaking spreads on those pairs are considerably higher than with the Forex majors. This can create significant obstacles for scalpers and day traders, who execute large numbers of trades on a daily basis. In addition to that due to inflation rate differentials, many exotic currencies are engaged in long term downward trends against the US dollar and other major currencies.